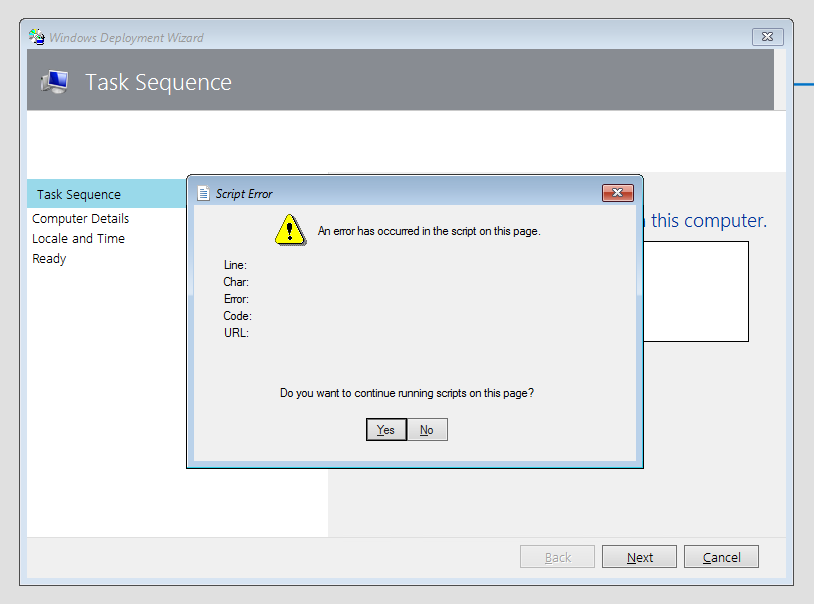
You may seen the above error when PXE booting images under the new Windows PE edition for Windows 11. Yes, frustrating right! Well this is what I did to fix the issue. Depending on how many WDS/MDT servers you have you may have to follow this multiple times.
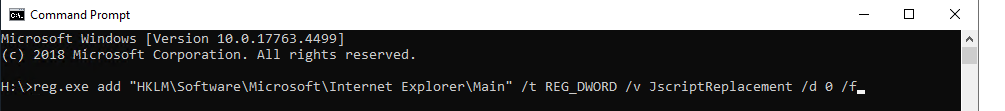
First you will want to open a new Command Prompt “CMD” window in Administrator mode. Type in the following reg.exe add”HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main” /t REG_DWORD /v JscriptReplacement /d 0 /f
Next Backup this C:\Program Files\Microsoft Deployment Toolkit\Templates\Unattend_PE_x64.xml file. Then edit the file with the code below and finally regenerate the entire WIM image. If you have more than one server you will have to follow these instructions again.
<unattend xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:unattend">
<settings pass="windowsPE">
<component name="Microsoft-Windows-Setup" processorArchitecture="amd64" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" language="neutral" versionScope="nonSxS" xmlns:wcm="http://schemas.microsoft.com/WMIConfig/2002/State">
<Display>
<ColorDepth>32</ColorDepth>
<HorizontalResolution>1024</HorizontalResolution>
<RefreshRate>60</RefreshRate>
<VerticalResolution>768</VerticalResolution>
</Display>
<RunSynchronous>
<RunSynchronousCommand wcm:action="add">
<Description>Lite Touch PE</Description>
<Order>1</Order>
<Path>reg.exe add "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Main" /t REG_DWORD /v JscriptReplacement /d 0 /f</Path>
</RunSynchronousCommand>
<RunSynchronousCommand wcm:action="add">
<Description>Lite Touch PE</Description>
<Order>2</Order>
<Path>wscript.exe X:\Deploy\Scripts\LiteTouch.wsf</Path>
</RunSynchronousCommand>
</RunSynchronous>
</component>
</settings>
</unattend>





